(A Spinal Cord Injury (SCI) Spinal cord injury (SCI) is an insult to the spinal cord resulting in a change, either temporary or permanent, in its normal motor, sensory, or autonomic function.
CAUSES
Motor accidents
Gunshot wounds
Falls/swimming accidents
MECHANISM
Forces that lead to spinal injury are:
⦁ Excessive flexion, extension, rotation, or compression of the vertebral column
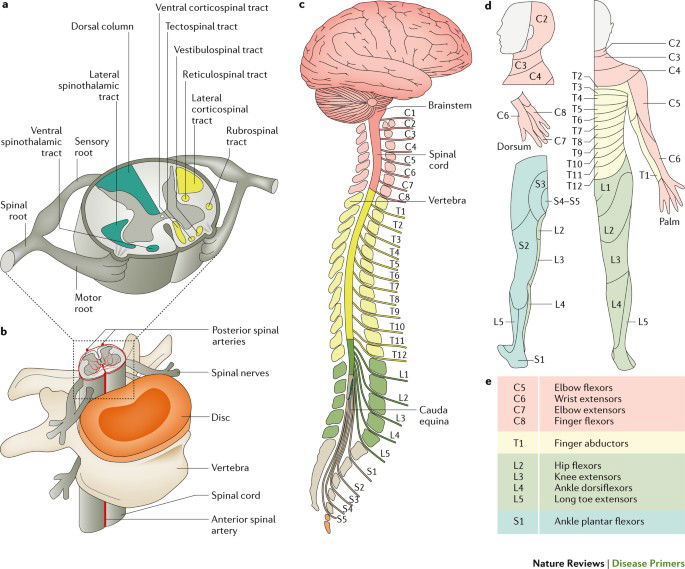
TYPES OF TISSUE DAMAGE
⦁ Primary, mechanical damage
⦁ Secondary, tissue damage
The secondary spinal cord damage begins within minutes of the primary damage. It is caused by ischemia, edema, and ion imbalances.
CLASSIFICATION
⦁ The entire cord or a portion
⦁ The level of the injury
Definitions of complete and incomplete SCI are based on the above ASIA definition with sacral-sparing.
⦁ Complete lesion – Absence of sensory and motor functions in the lowest sacral segments
⦁ Incomplete lesion- Preservation of sensory or motor function below
⦁ level of injury, including the lowest sacral segments
The extent of injury is defined by the ASIA Impairment Scale (modified from the Frankel classification), using the following categories:
⦁ A - Complete: No sensory or motor function is preserved in sacral segments S4-S5.
⦁ B - Incomplete: Sensory, but not motor, function is preserved below the neurologic level and extends through sacral segments S4-S5.
⦁ C - Incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurologic level, and most key muscles below the neurologic level have muscle grade less than 3.
⦁ D - Incomplete: Motor function is preserved below the neurologic level, and most key muscles below the neurologic level have muscle grade greater than or equal to 3.
⦁ E - Normal: Sensory and motor functions are normal